Table of Contents
The digitization of health information and adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) have revolutionized patient data management. While medical transcription services are practical approach to guarantee precise and timely EHR documentation, achieving EHR interoperability – the capability to exchange EHR data among healthcare providers – is vital. EHR interoperability facilitates seamless sharing of information and improves health care delivery by making data available at the right time to the right people.
Even as demand for enhanced patient care is increasing, the goal of seamless data exchange in healthcare remains challenging, according to a Forbes article titled “Healthcare Interoperability Considerations We Can’t Ignore In 2024”. The article, published in Jan this year, noted that Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) reported that though 88% of hospitals used electronic data exchange in 2021, almost half of the hospitals (48%) share patient data with other providers but don’t receive data from them.
Let’s explore the benefits for EHR interoperability, its challenges and the solutions.
Essential Components of EHR Interoperability
The Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) defines interoperability as the extent to which systems and devices can exchange data, and interpret that shared data. One of the goals of the World Health Organization’s Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025 is creating an interoperable digital health ecosystem.
According to WHO, “An interoperable digital health ecosystem should enable the seamless and secure exchange of health data by and between users, health care providers, health systems managers, and health data services.” WHO recognizes interoperability as one of the main principles of how digital health should work.
EHR interoperability requires healthcare organizations to adopt and adhere to technical standards, such as the Health Level Seven International (HL7) standard, which defines a common language for exchanging health information. They also need to develop policies that govern the collection, use, and sharing of health data to ensure patient privacy and security. The 21st Century Cures Act aims to promote health data interoperability by requiring healthcare organizations to allow patients to access and share their health data electronically.
Importance of EHR Interoperability
Seamless sharing of patient health information across providers, payers, patients, and locations is vital for improving care, reducing errors, and enhancing population health management. When health data is siloed, it leads to fragmented care and poor coordination, affecting patient outcomes. With an aging population and rising chronic conditions, interoperability and data sharing are crucial for effective healthcare. The AHRQ estimates that two-thirds of older Americans have multiple chronic conditions, driving up healthcare costs. Effective data interoperability is key to a more connected, patient-centered healthcare system.
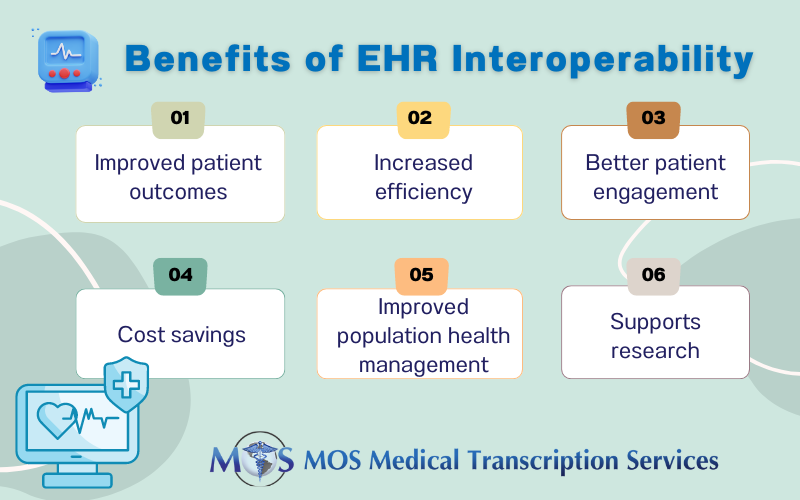
The benefits of health data interoperability include:
- Improved patient outcomes: When healthcare providers have access complete and up-to-date patient information it can drive informed treatment decisions, improved care coordination, and better care outcomes.
- Increased efficiency: Interoperability enables more efficient care delivery and reduced administrative burden by reducing the time and resources required to share health data between different providers
- Better patient engagement: When patients have access to their health data and can share it with different providers and healthcare organizations, it can improve patient engagement and support more personalized care.
- Cost savings: By preventing medical errors, reducing unnecessary tests and procedures, and improving care coordination, interoperability can lead to cost savings for providers and patients.
- Improved population health management: When healthcare organizations can aggregate and analyze health data across different systems, it can inform population health management strategies and support public health initiatives.
- Supports research: By allowing for the use of large-scale, real-world data sets, interoperability helps the development of new treatments and technologies.
Challenges to EHR Interoperability and Solutions
Achieving healthcare interoperability is crucial for effective clinical decision-making. Here are some of the challenges to achieving this goal and the solutions:
- Lack of standardization: Although standards like FHIR and HL7 and APIs are designed to enhance interoperability, many providers still use customized EHR systems that resist standardization. Developing APIs for secure, efficient data exchange can address this issue.
- Patient privacy concerns: Balancing data accessibility with security is challenging due to increasing cybersecurity threats. Ensuring robust privacy measures and compliance with regulations is essential to prevent breaches and protect patient information.
- Data management issues: Inconsistent data across large networks complicates data retrieval and management. Effective integration technologies and analytics solutions can streamline data handling and improve coordination.
- Varied data formats and data quality issues: Although standards like FHIR and HL7 and APIs are designed to enhance interoperability, many providers still use customized EHR systems that resist standardization. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) states that establishing an interoperable health IT environment requires standardizing four key areas of EHR technology:
- 1. User interaction with applications (e.g., e-prescribing)
- 2. Communication between systems (e.g., messaging standards)
- 3. Information processing and management (e.g., health information exchange)
- 4. Integration of consumer devices with other systems and applications (e.g., tablet PCs)
Inaccuracies, irrelevant data, and other quality problems in text, digital, audio, and graphic formats also pose a major challenge.
- Patient consent: Legal and ethical requirements for patient consent complicate data sharing. Clear guidelines and informed consent processes are necessary to navigate privacy concerns while facilitating information flow.
- Financial constraints: Implementing and maintaining interoperable EHR systems is costly, involving software, hardware, training, and ongoing upgrades. Financial investment is needed to support data conversion and migration efforts.
The following measures can provide solutions to address these challenges:
- Implementing common data exchange standards like HL7 and FHIR
- Developing APIs for secure, efficient data exchange
- Using machine learning to improve data quality and accessibility
- Ensuring stringent measures to safeguard patient information.
- Making health data accessible and understandable to patients for informed consent
- Obtaining explicit patient consent for information sharing
- Investing in integration technologies and analytics solutions
Achieving Interoperability: Importance of Collective Action
Achieving interoperability requires collective action by all stakeholders: healthcare providers, patients and technology developers. To facilitate seamless data exchange and enhanced patient care, practice managers should keep interoperability at the forefront of their requirements when selecting an EHR. Cloud-based EHRs enable easy integration and access to various data sources, including clinical, lab, and pharmacy systems, ensuring interoperability and improving the quality of care for patients. These EHRs also allow for storing of data on multiple servers across different geographical locations, enabling retrieval of data as needed. They also come with advanced security features to protect against cyberattacks and unauthorized access to sensitive patient data.
As patient data is shared across healthcare systems and organizations, ensuring accuracy and timeliness in the information is crucial. Healthcare providers can partner with a reliable medical transcription company to maintain up-to-date and accurate EHR data to support clinical decision-making and patient care.


