Table of Contents
Electronic health records (EHRs) are designed to enable physicians to efficiently manage and access comprehensive patient information digitally. EHRs provide a centralized platform for storing medical histories, treatment plans, medications, and test results. However, entering and registering patients’ data in their EHRs can take up to 40–50% of the physician’s time during working hours. This has led most providers to turn to HIPPA-compliant medical transcription companies to better manage their EHR documentation needs. Though outsourcing medical transcription is a practical solution to ensure accurate EHR data entry, studies say that poor EHR design can lead to errors that compromise patient safety.
EHR Usability Issues: What Studies Found
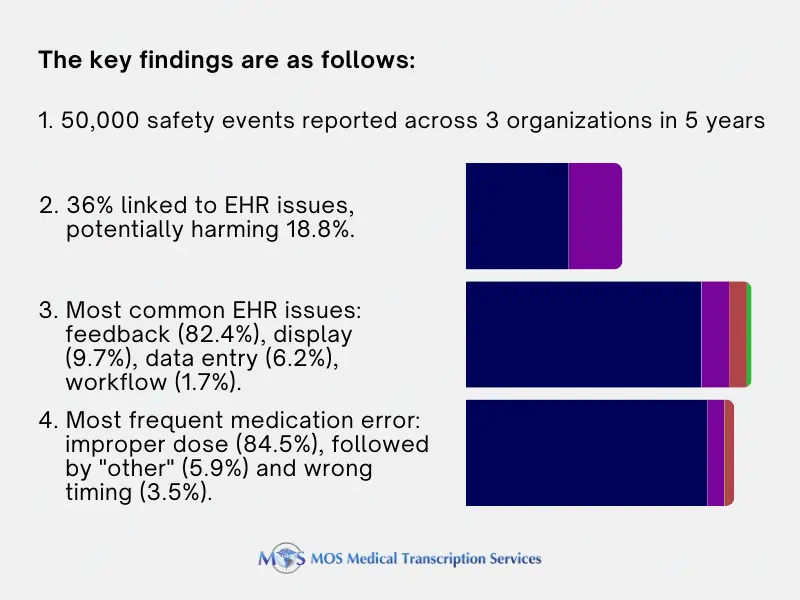
A study published in Health Affairs found that usability of EHRs accounted for more than a third of medication errors noted in 9000 pediatric patient safety event reports. Led by Raj Ratwani, director of the National Center for Human Factors in Healthcare at MedStar Health, the study defined usability as “the extent to which the technology can be used efficiently, effectively, and satisfactorily” based on system design and customization to specific workflows. With physical characteristics that differ from adults, children may be at greater risk of harm from poor EHR usability.
The four general usability categories and warning signals for EHRs were listed as: System feedback (inappropriate), Visual display (clear, confusing, or cluttered), Data entry (difficult or impossible), and EHR workflow and clinician expectations (mismatch).
The study looked into nine types of medical errors defined by the National Medication Errors Reporting Program of the National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention: improper dose, wrong strength/concentration, wrong drug, wrong dosage form/technique/route, wrong rate, wrong time, wrong patient, monitoring error, and “other”. The team found that the general pattern of usability challenges and medication errors were similar across the three sites.
The researchers recommended that Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) add safety with the voluntary certification criteria of EHRs for use with children and include usability measures to assess EHR performance.
In December 2023, the American Medical Association reported on a JAMA study that highlighted these challenges and more in EHR use based on an analysis of 557 reports from healthcare professionals:
- Data entry: Clinicians face difficulty entering accurate EHR data, leading to errors such as selecting the wrong frequency for medication administration.
- Alerting: Inadequate EHR alerts contribute to issues like overlooking patient allergies while prescribing medication.
- Interoperability: Insufficient interoperability within EHR components or with external systems hampers information exchange, impeding access to vital data like laboratory results.
- Visual display: Complex, cluttered, or inaccurate EHR displays make it challenging for clinicians to interpret information correctly.
- Availability of information: Critical information is hindered due to incorrect entry, storage location, or inaccessibility within the EHR, impacting tasks like ordering diagnostic tests.
- System automation and defaults: Unexpected or non-transparent automated defaults in the EHR, such as date settings, can lead to errors in medication orders.
- Workflow support: Mismatches between EHR workflows and user intent, like essential instructions being unnoticed by lab staff, result in breakdowns in processes, affecting tasks such as diagnostic test orders.
The report suggests that healthcare providers and EHR developers adopt safety-focused, stringent test case scenarios outlined in the report. This approach aims to identify and rectify issues, thereby preventing patient safety concerns.
Clinician Stress leading to EHR Documentation Errors
A study in JAMIA, for instance, revealed that for every eight hours office-based physicians allocate to patient appointments, over five hours are spent navigating the EHR. Practitioners and nurses burdened with heavy workloads might import inaccurate medication lists into EHRs, unintentionally transmitting erroneous information through electronic copying and pasting of older record sections, or input incorrect examination findings. Other common errors linked to EHR documentation include:
- Not documenting patient history
- Not recording allergies leading to prescribing errors
- Prescribing errors can involve the wrong dose, form, quantity, administration route, concentration, or rate of admission
- Communication breakdowns leading to lack of clarity on current or updated information, which could result in an overdose
- Omitting to give the medication before the next one is scheduled
- Giving a medication outside the predetermined interval
- Wrong formulation of a medication
EHR documentation errors could lead to various issues, including wasteful duplication, unnecessary or incorrect treatment, and delayed diagnoses, among other potential problems.
It is critical to resolve EHR usability concerns and ensure access to reliable medication histories by subsequent caregivers. Accurate documentation translates to accurate recording of information such as the name of the drug, the dose, route, time, patient response, and any refusal of the drug by the patient. With advanced systems, physicians can make more informed decisions, improve collaboration among healthcare teams, and ensure accurate and up-to-date patient data, potentially fostering improved care delivery.
The AMA reports that an increasing body of evidence is quantifying how EHRs add to physicians’ clerical burdens and contributing to the crisis of doctor burnout. Initiated in 2019, the AMA’s Electronic Health Record Use Research Grant Program aims to identify EHR usage patterns that may undermine patient care.
Medical transcription services can play an important role in improving provider transcription. Investing in experienced transcriptionists can ensure accurate and timely medical records. This can empower clinicians to provide better care and reduce medication errors, leading to safer patient outcomes.