Hospitals and medical practices are increasingly using speech recognition technology to implement more efficient documentation workflows and cut costs. Speech recognition systems allow healthcare providers to use their own voice to log information directly into the electronic health record (EHR). Nevertheless, while speech recognition tools expedite the clinical documentation process, they are not perfect and may not be sufficient for ensuring comprehensive and error-free medical records. As a result, providers often rely on human-based medical transcription services to enhance the accuracy of machine-generated documentation.
Hospitals and medical practices are increasingly using speech recognition technology to implement more efficient documentation workflows and cut costs. Speech recognition systems allow healthcare providers to use their own voice to log information directly into the electronic health record (EHR). Nevertheless, while speech recognition tools expedite the clinical documentation process, they are not perfect and may not be sufficient for ensuring comprehensive and error-free medical records. As a result, providers often rely on human-based medical transcription services to enhance the accuracy of machine-generated documentation.
Table of Contents
According to Statista, the global speech recognition market size will reach a value of US$4.83bn by 2030. The report estimated that the United States would have the largest market size in 2024, valued at US$1,903.00m. The increasing demand for speech recognition technology in healthcare is a major growth factor for the speech recognition market.
While speech recognition technology offers numerous advantages in the healthcare setting, physicians should also be aware of its limitations.
How does Medical Speech Recognition Work?
Speech recognition software digitizes your speech. It converts your speech into sound waves and then compiles it into recognizable words and phrases. Beyond mere transcription, advanced speech recognition tools leverage natural language processing (NLP) to “understand” the context and meaning behind your words.
When speech recognition technology is integrated directly into the EHR system, it enables healthcare providers to complete their entire medical note using only their voice, without having to manually type or enter information. The software automatically transcribes the provider’s dictation and enters the information in the relevant fields and sections of the patient’s electronic chart.
There are two broad categories of speech recognition systems: traditional speech recognition software and AI medical scribes. The traditional software types as the physician dictates. AI-powered medical scribes go further by leveraging NLP. The AI listens to physician-patient conversations and automatically generates complete transcripts with all the relevant details discussed, including helpful suggestions.
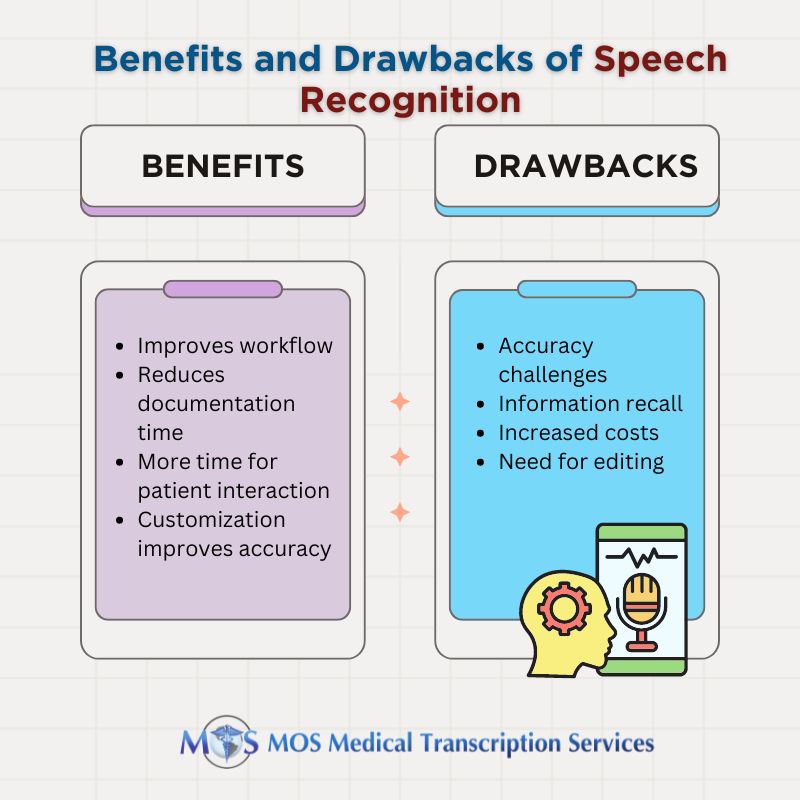
Benefits and Drawbacks of Speech Recognition for Medical Transcription
First, let’s consider the benefits of speech recognition technology in the clinical setting:
- Improves workflow: The seamless integration of speech recognition into the EHR creates a truly hands-free, voice-driven clinical documentation workflow. This can improve efficiency and reduce the data entry burden, leaving more time for direct patient interaction.
- Reduces documentation time: One of the key benefits of speech recognition is that it can help to reduce documentation time. Traditional medical documentation, where clinicians manually type or write patient notes, can be a time-consuming process that detracts from direct patient care. Speech recognition allows providers to dictate their observations, diagnoses, and treatment plans directly into the electronic health record (EHR) system. This real-time voice-to-text conversion can significantly speed up the documentation workflow compared to manual typing. Studies have shown that speech recognition can reduce documentation time by 30-50% compared to keyboard-based entry.
- More time for patient interaction: Speech recognition allows clinicians to spend more time with patients, leading to better conversations about their condition and care. This extra time can enhance patient interactions and improve health outcomes.
- Customization improves accuracy: Medical speech recognition systems adapt to your unique voice and medical terms the more you use them. They also work for multiple users, learning from different voices and inputs to become more accurate over time.
Now, let’s consider the drawbacks.
- Accuracy challenges: Using speech recognition for transcription comes with several challenges: The software may struggle with:
- comprehending specialized medical terms and jargon
- variations in accents and dialects
- differences in individual voice patterns and speech rhythms
- complex sentences or fast speech
- context-specific meanings and nuances in medical conversations
Additionally, background noise or overlapping conversations can interfere with the system’s ability to capture clear audio. Addressing the above-listed challenges and improving accuracy often includes continual customization, training, and integration with specialized medical vocabularies.
- Information recall: A major issue with speech recognition is the risk of forgetting important details discussed during the patient encounter. If you rely solely on speech recognition to dictate your notes, you may not be actively engaged in the physical act of writing or typing. When you are more focused on speaking the notes, it can affect how you process and retain the information. This might lead you to forget some of the information discussed with the patient, which can affect the accuracy of the final documentation.
- Burdensome: Dictating medical information using speech recognition can be burdensome for providers. Since the technology often requires dictating even basic punctuation, it can become exhausting. For example, when updating the patient’s record, the physician might have to say: “The patient presents with headaches comma nausea comma and dizziness period.” After a long day of seeing many patients, verbally specifying punctuation to format the text correctly can be very tiring.
- Cost: Speech recognition technology is expensive to set up. Before investing in the software, you need to consider the initial infrastructure requirements, future technology upgrades, and maintenance costs.
- Need for editing: As explained earlier, speech recognition technology cause errors in the transcript due to misinterpretation of medical terms, variations in pronunciation or speech patterns, lack of contextual understanding, failure to capture specialized terms, and formatting issues. All of this necessitates manual corrections in automatic transcriptions.
The bottom line is that speech recognition software requires human intervention to guarantee the highest accuracy. However, it would be impractical and time-consuming for physicians to proofread and check their own transcripts. Fortunately, they can rely on a medical transcription company to review, edit, and correct the reports generated by these applications. Leading companies have stringent quality assurance checks to ensure top accuracy.
The use of EHR-integrated speech recognition in combination with human based medical transcription can generate legible, comprehensive documentation that improves the quality of patient care and creates efficiencies for the health care organization.