Table of Contents
Accurate documentation is a critical factor for smooth collaboration among healthcare providers. Transcribing physician notes into standardized digital documents requires comprehensive, up-to-date knowledge of medical terminology. In fact, one of the most important considerations when outsourcing medical transcription is choosing a skilled and experienced service provider. Given the complexity and sensitivity of medical information, the need for accuracy, confidentiality, and up-to-date knowledge in this field cannot be overstated. Even small errors can have significant consequences, making continuous learning essential for medical transcription professionals.
Overview of Different Types of Medical Transcription Reports
Medical transcriptionists assist in creating various types of reports essential for patient records:
- 1. Physical and History Report: Created upon a patient’s hospital admission, this report outlines the main complaint, medical history, system reviews, and physical exam findings. It concludes with the treatment plan and admission diagnosis.
- 2. Consultation Report: Written by a specialist consulted by the admitting doctor, it includes the patient’s symptoms, relevant exam findings, and may feature lab or imaging results. The report ends with the consulting physician’s assessment and treatment recommendations.
- 3. Operative Report: Dictated by the surgeon, this report details the surgical procedure, including pre- and postoperative diagnoses, the surgical team, anesthesia type, and a step-by-step description of the operation. It also notes postoperative patient status and where they were taken post-surgery.
- 4. Radiology Report: Following a diagnostic imaging procedure, the radiologist provides observations and impressions from scans such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
- 5. Pathology Report: Summarizes findings from a tissue sample, focusing on microscopic examination and pathological diagnosis.
- 6. Laboratory Report: Documents the results of tests on fluids like blood or urine, often integrated within other reports such as H&P or discharge summaries.
- 7. Miscellaneous Reports: These include any additional documents related to patient care not covered in the primary categories.
These reports ensure accurate, detailed records of a patient’s care and treatment across various stages and specialties.
Staying Updated with Medical Terminology
Medicine is constantly evolving and so is medical terminology. Several thousand new medical terms are created each year, according to the World Health Organization. Primary healthcare terminologies key to data analysis have seen major changes, such as updates to Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
Medical terminology includes eponyms, acronyms, and modern language English terms. For example, Parkinson’s disease is an eponym, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is an acronym, and nuclear medicine scanner is a modern language English term. Medical transcriptionists need to be familiar with such diverse terms used in modern healthcare.
Continuous learning helps transcriptionists stay informed about emerging terms, diagnoses, and treatment methods, enabling them to accurately transcribe complex notes. Familiarity with the latest terms is crucial to avoid making coding or billing errors and misunderstandings that could affect patient care.
Ensuring Accuracy in Documentation
Medical transcriptionists often handle documentation for various specialties, each with its unique terminology and standards. Their primary goal is to accurately convey the terms, which is why it is so essential that they possess a thorough knowledge of the medical content that they are working with. For instance, in specialties like radiology, cardiology, or oncology, understanding nuances improves transcription quality and ensures accurate representation of the specifics in the documentation.
Continuous learning enhances the versatility and employability of these professionals. In addition to regular training, they often read medical journals to stay current with new developments, refer to updated medical dictionaries, and consult medical terminology databases consistently. Since they listen to physician dictation, they also need to verify the pronunciation of new terminology.
Continuous learning also allows transcriptionists to enhance their language and grammar skills. This enables them to consistently produce error-free documents, which is especially important for non-native medical terms or complex sentence structures often seen in medical notes. Precision is paramount to prevent costly transcription errors such as miscommunication of medical terms, which can lead to a poor patient experience, and increased workload and stress.
Enhancing Compliance and Data Security Skills
As data privacy regulations like HIPAA evolve, transcriptionists must stay informed to ensure that their work adheres to the latest compliance standards. HIPAA-compliant medical transcription safeguards sensitive patient data by ensuring confidentiality and preventing unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. Failure to comply can lead to serious legal repercussions, reputational harm, and risks to patient privacy. Regularly updating knowledge in these areas helps prevent security breaches, ensure proper handling of sensitive information, and align with industry best practices for data protection.
Staying Updated with New Transcription Methods
With the introduction of new transcription methods and evolving technology, medical transcription has undergone significant advancements in recent years. Innovations in the field include:
- Voice recognition software
- Automated transcription with AI
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) in EHR systems
- Remote and mobile transcription solutions
- Enhanced audio processing and noise reduction functionalities
Ongoing learning is essential for transcriptionists to stay current with these changes and remain efficient and relevant in the field. For example, modern voice recognition technology leverages AI to understand medical terms and context better than earlier models. Since these tools still require human oversight for accuracy and context, transcriptionists must know how to edit and refine speech-to-text documentation.
By staying updated with these emerging trends makes it possible for medical transcriptionists to:
- Ensure they’re using the latest tools and techniques for faster, more accurate transcriptions.
- Adapt to new industry standards, such as updates to HIPAA and data security protocols.
- Improve their efficiency by learning shortcuts, advanced editing techniques, and software features.
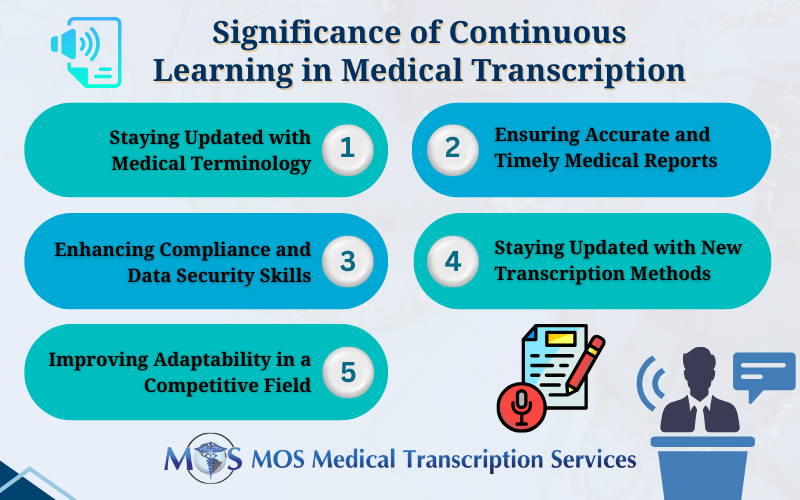
The medical transcription field demands a commitment to lifelong learning. For a medical transcription company, this means ensuring that their teams staying current with medical language, evolving technology, and regulatory standards to deliver accurate, compliant, and effective documentation. Physicians should partner with medical transcription companies that ensure their transcriptionists are equipped with the skills needed to ensure accurate, timely documentation that supports high quality patient care.